Lead Management
Lead Enrichment: Enhancing Lead Data for Better Qualification
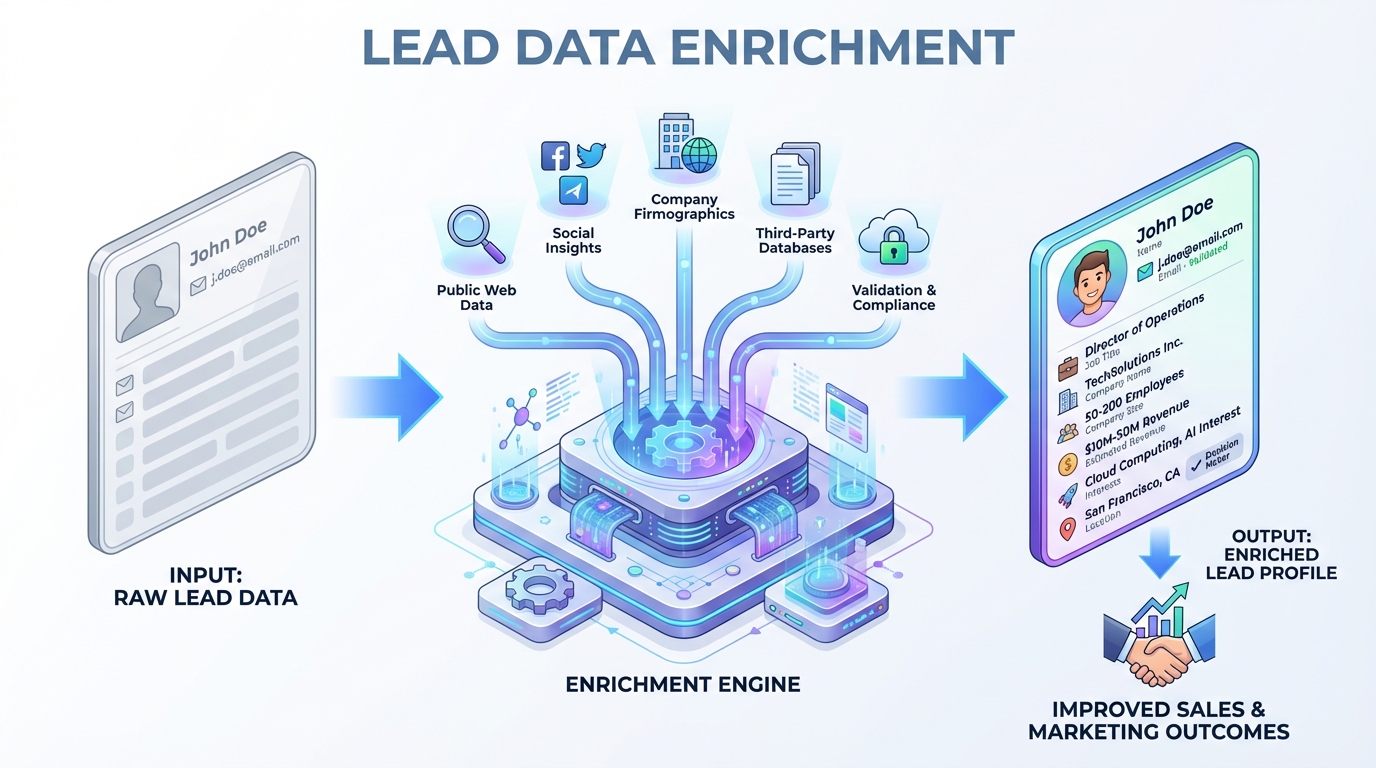
A lead submits a form with just a name and email. Your sales rep receives the assignment with no context: no company size, no industry, no job title, no indication whether this is a qualified prospect or a student researching a paper.
Without enriched data, every lead requires manual research before outreach. Sales reps spend hours per day on LinkedIn and Google, hunting for information that enrichment tools could provide instantly. Meanwhile, hot leads cool while reps investigate.
Lead enrichment turns incomplete inquiries into actionable intelligence. It's the operational layer between lead capture and lead routing that determines whether your sales team engages informed and prepared, or wastes time on blind outreach.
Key Facts: The Data Quality Crisis in B2B Sales
- 70% of CRM data is outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate at any given time, according to DealSignal's Sales Performance research - meaning most companies are making qualification and routing decisions on fundamentally flawed information.
- B2B contact databases decay at 2.1% per month, compounding to roughly 22.5% annually (IndustrySelect). Job titles alone change at 65.8% per year, making unenriched lead records unreliable within months of capture.
- Poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million per year, according to Gartner - a figure driven by targeting errors, wasted rep time, and missed opportunities on qualified prospects.
- Sales reps waste approximately 500 hours per year (equivalent to 62 working days) correcting bad prospect data and manually researching leads before outreach, per DealSignal research.
- Companies that address CRM data decay see a 15% improvement in close rates within six months, along with a 20% improvement in campaign response rates (SMARTe).
What is Lead Enrichment?
Lead enrichment is the process of appending additional data to captured leads by matching contact information (email, company domain, phone) against third-party databases or public sources.
Input: Name, email (minimal form submission)
Output: Name, email, title, seniority, department, company name, company size, industry, revenue, location, technology stack, social profiles
Enrichment fills the gaps between what prospects provide and what sales needs for qualification and personalization.
Why Enrichment Matters: Four Operational Outcomes
Lead enrichment isn't about collecting data for data's sake. It delivers four measurable operational improvements:
1. Better Qualification
The problem: Can't score or qualify leads without firmographic data.
The solution: Enriched company size, industry, and revenue make automated ICP matching and lead scoring possible.
Result: Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) are actually qualified. Sales doesn't waste time on students, competitors, or wrong-fit companies.
Example: A form submission with just name and email scores 20/100 (unknown fit). After enrichment reveals it's a Series B SaaS company with 150 employees in your target industry, the score jumps to 85/100 (high priority).
2. Improved Personalization
The problem: Generic outreach ("Hi, I saw you visited our website") doesn't resonate.
The solution: Enriched title, industry, and company data let you personalize your messaging.
Result: Higher response rates and faster progression through qualification.
Example:
- Generic: "Hi Sarah, thanks for downloading our guide. Want to chat?"
- Personalized: "Hi Sarah, I saw you're leading growth marketing at a 50-person fintech. Many of our customers in your segment use our platform to accelerate their lead-to-MQL conversion. Worth a quick conversation?"
3. Faster Routing
The problem: Can't route by territory or specialization without company location and industry.
The solution: Enriched data lets you build sophisticated routing rules. Route enterprise to enterprise reps, healthcare to healthcare specialists, EMEA to EMEA team.
Result: Leads reach the right person faster, with better context and higher conversion potential.
4. Higher Conversion
The combination: Better qualification + improved personalization + faster routing equals measurably higher conversion.
Benchmarks: Organizations using enrichment report:
- 20-30% improvement in lead-to-opportunity conversion (Datamaticsbpm B2B Data Solutions research)
- 15-25% increase in email response rates through better personalization (industry consensus across enrichment platforms)
- 25-40% reduction in time spent researching prospects, consistent with DealSignal's finding that reps waste ~500 hours annually on bad data without enrichment
What Data Should You Enrich?
Enrichment providers append dozens of data points. Prioritize based on operational value:
Contact-Level Data (Individual)
Job title: Role and position (VP of Marketing, Software Engineer, CEO)
- Why it matters: Determines authority and relevance
- Use cases: Qualification scoring, routing to appropriate rep level
Seniority level: C-level, VP, Director, Manager, IC
- Why it matters: Indicates decision-making authority
- Use cases: Prioritization, sales approach customization
Department/Function: Marketing, Engineering, Sales, Finance, Operations
- Why it matters: Aligns outreach to functional priorities
- Use cases: Personalization, use case messaging
Location: City, state, country, time zone
- Why it matters: Territory routing, meeting scheduling, localization
- Use cases: Geographic routing, appropriate contact time
Social profiles: LinkedIn, Twitter, GitHub URLs
- Why it matters: Research, relationship building, social selling
- Use cases: Pre-call research, warm introduction paths
Company-Level Data (Firmographic)
Company name: Full legal name with normalization
- Why it matters: Foundation for all other firmographic enrichment
- Use cases: Deduplication, account-based routing
Company size: Employee count or ranges (1-10, 11-50, 51-200, 201-500, 500+)
- Why it matters: Primary ICP filter for most B2B companies
- Use cases: Segment routing (SMB vs Enterprise), qualification scoring
Industry/Sector: Vertical market classification (SaaS, Healthcare, Financial Services)
- Why it matters: Product fit, use case relevance, vertical specialization
- Use cases: Industry-specific routing, vertical messaging
Annual revenue: Estimated or reported revenue ranges
- Why it matters: Budget capacity, deal size potential
- Use cases: Enterprise vs SMB routing, pricing approach
Company location: Headquarters and office locations
- Why it matters: Geographic routing, compliance considerations
- Use cases: Territory assignment, regional pricing
Funding stage: Bootstrapped, Seed, Series A/B/C, Public
- Why it matters: Budget availability, growth trajectory
- Use cases: Pricing strategy, priority scoring
Technographic Data
Technology stack: Software and tools currently used
- Why it matters: Competitive displacement opportunities, integration possibilities
- Use cases: Competitive battle cards, integration messaging
CRM platform: Salesforce, HubSpot, Pipedrive, etc.
- Why it matters: Integration requirements, migration complexity
- Use cases: Implementation planning, compatibility messaging
Marketing automation: Marketo, Eloqua, Pardot, etc.
- Why it matters: Integration compatibility, sophistication level
- Use cases: Technical fit assessment, integration roadmap
Hosting/Infrastructure: AWS, Azure, GCP, on-premise
- Why it matters: Technical requirements, deployment model
- Use cases: Architecture discussions, compliance requirements
Intent Signals
Content consumption: Topics researched, content downloaded
- Why it matters: Indicates current priorities and pain points
- Use cases: Conversation starters, pain-point messaging
Website behavior: Pages visited, time spent, repeat visits
- Why it matters: Buying stage indicators, engagement level
- Use cases: Hot lead prioritization, engagement scoring
Competitor research: Engagement with competitor content
- Why it matters: Active evaluation, potential switching intent
- Use cases: Competitive positioning, urgency messaging
Trigger events: Funding, hiring, leadership changes, expansion
- Why it matters: Timing indicators for outreach
- Use cases: Relevance and timeliness in outreach
How to Enrich Lead Data
Four approaches to enriching lead data, each with trade-offs:
1. Manual Research (Low Scale, High Quality)
What it is: Sales reps manually research leads using LinkedIn, company websites, and Google.
Pros:
- 100% accuracy when done correctly
- Contextual insights beyond data fields
- No cost beyond rep time
Cons:
- Doesn't scale (takes 5-15 minutes per lead)
- Inconsistent execution and completeness
- Delays lead routing and follow-up
- Wastes expensive sales time
When to use: High-value strategic accounts only.
2. Progressive Profiling (Over Time)
What it is: Gradually collecting additional data across multiple form submissions and interactions rather than asking for everything upfront.
How it works: First form asks name/email. Second form asks company/title. Third form asks company size/industry. Each interaction enriches the profile.
Pros:
- Higher initial conversion (fewer form fields)
- User-provided data (100% accurate)
- Natural engagement progression
Cons:
- Needs multiple interactions to complete the profile
- Delays qualification and routing
- Only enriches engaged leads
When to use: Long nurture cycles with content-heavy engagement strategies.
3. Third-Party Data Providers (Scale + Automation)
What it is: Automated enrichment via API calls to data providers (ZoomInfo, Clearbit, Apollo, Lusha, FullContact).
How it works: Send email or company domain to provider API. Receive enriched data fields in response. Append to lead record.
Pros:
- Instant enrichment (sub-second API response)
- Scales to unlimited volume
- Comprehensive data coverage
- Makes real-time qualification and routing possible
Cons:
- Costs money per enrichment (per lead or per credit)
- Data accuracy varies by provider (70-90% match rate typical)
- Privacy and compliance considerations
- Requires API integration and maintenance
When to use: High-volume lead flows requiring instant qualification and routing.
Popular providers:
- ZoomInfo: Largest B2B database, comprehensive company and contact data
- Clearbit: Real-time enrichment, strong company data, lower contact coverage
- Apollo: Combined enrichment and outreach platform, competitive pricing
- Lusha: Contact-focused, strong email and phone data
- FullContact: Consumer and B2B, social profile enrichment
4. Reverse IP Lookup (Company Identification)
What it is: Identifying companies visiting your website based on IP address, even if they don't submit a form.
How it works: Capture website visitor IP address. Match against database of company IP ranges. Identify company name and firmographic data.
Pros:
- Identifies anonymous website traffic
- Uncovers account-level intent before form submission
- Lets you reach out proactively
Cons:
- Company-level only (no individual contact data)
- Doesn't work for remote workers or residential IPs
- Lower accuracy (around 60-70% match rate)
- Privacy concerns in some regions
When to use: Account-based marketing strategies, intent signal capture.
Popular providers: Clearbit Reveal, Demandbase, 6sense, Leadfeeder
5. Social Enrichment
What it is: Appending social profile data (LinkedIn, Twitter, GitHub) to lead records.
How it works: Match name and company to social profiles. Extract profile data and URLs.
Pros:
- Valuable for research and relationship building
- Supports social selling approaches
- Often free or low-cost
Cons:
- Match accuracy varies with common names
- Profile data may be outdated
- Limited firmographic depth
When to use: Sales development and social selling workflows.
When to Enrich: Timing Strategies
Enrichment timing affects data quality, routing speed, and costs:
At Capture (Real-Time)
When: Immediately upon form submission or lead creation, before routing.
Advantages:
- Lets you build sophisticated routing rules (territory, account-based, ICP priority)
- Immediate lead scoring and qualification
- Sales receives complete context
Disadvantages:
- Adds latency to form submission (typically 2-5 seconds)
- Higher API costs (enriching every lead including junk)
- Potential user experience impact if enrichment fails
Best for: High-intent lead sources (demo requests, contact sales, event registration).
After Capture (Batch)
When: Minutes to hours after lead creation, during background processing.
Advantages:
- No impact on form submission user experience
- Opportunity to deduplicate before enriching (cost savings)
- Can retry failed enrichments without user impact
Disadvantages:
- Delays routing (minutes to hours)
- Can't use enriched data for real-time routing rules
- Requires batch processing infrastructure
Best for: Lower-intent sources (content downloads, newsletter signups).
Before Routing (Enrichment Gate)
When: After initial capture but before assignment to sales rep.
Advantages:
- Ensures sales never receives incomplete lead data
- Optimizes cost by enriching only qualified leads
- Can implement enrichment fallback strategies
Disadvantages:
- Adds 5-30 seconds to routing latency
- Creates dependency on enrichment provider availability
- Requires fallback logic for enrichment failures
Best for: Organizations prioritizing complete data over routing speed.
Before Sales Touch (Just-in-Time)
When: After routing but before sales rep's first outreach attempt.
Advantages:
- Most cost-efficient (only enriching leads that reach sales)
- Freshest data at point of use
- No impact on routing latency
Disadvantages:
- Can't use enriched data for routing or scoring
- Rep waits for enrichment before outreach
- Requires rep workflow integration
Best for: Organizations with high junk lead volume or strict cost controls. Learn more about lead response time optimization.
Data Quality: Accuracy, Freshness, Completeness
Enrichment quality varies significantly by provider and data type:
Match Rates (What Percentage of Leads Can Be Enriched?)
Email match rates:
- B2B work emails: 70-85%
- Personal emails (Gmail, Yahoo): 10-30%
- Obscure domains: 40-60%
Company domain match rates:
- Established companies (500+ employees): 90-95%
- Startups and SMBs: 60-75%
- Non-profits and government: 50-70%
Best practice: Test multiple providers on your actual lead data before you commit.
Data Accuracy (How Correct is Enriched Data?)
Firmographic accuracy: 85-95% (company size, industry, revenue) Contact title accuracy: 70-85% (job changes are frequent) Contact seniority accuracy: 80-90% (more stable than exact title) Technology stack accuracy: 60-80% (detection is probabilistic)
Best practice: Implement data quality monitoring and feedback loops from sales.
Data Freshness (How Current is the Data?)
Update frequency: Varies by provider
- ZoomInfo: Quarterly updates typical
- Clearbit: Real-time enrichment from live sources
- Apollo: Monthly updates
Decay rates: Contact data decays rapidly (IndustrySelect research on B2B contact databases):
- Job title changes: 65.8% annually
- Phone numbers: 42.9% change annually
- Email addresses: 37.3% change annually
Best practice: Re-enrich leads periodically, especially for long nurture cycles.
Completeness (How Many Fields Are Populated?)
Enrichment rarely populates all fields. Expect:
- Core firmographics (company size, industry): 70-90% coverage
- Contact title and seniority: 60-80% coverage
- Technographics: 30-50% coverage
- Intent signals: 10-30% coverage (requires additional tools)
Best practice: Prioritize high-value fields and implement fallback strategies for missing data. Proper lead data management ensures data quality over time.
Privacy & Compliance: GDPR, Consent, Data Sources
Lead enrichment introduces compliance considerations, especially in EU markets:
GDPR Compliance
Key requirements:
- Lawful basis: Legitimate interest for B2B contact data (enriching business emails for business purposes)
- Transparency: Your privacy policy should disclose enrichment practices
- Data minimization: Only enrich fields you need for business purposes
- Right to deletion: Provide the ability to remove enriched data upon request
Best practices:
- Work with providers that certify GDPR compliance
- Document your legitimate interest assessment
- Provide opt-out mechanisms
- Maintain data processing agreements (DPAs) with providers
Data Source Transparency
Know where enriched data comes from:
- Public sources: LinkedIn, company websites, press releases (lower risk)
- User-contributed: Data shared by users on platforms (medium risk)
- Third-party purchases: Data aggregated from other vendors (higher risk)
Best practice: Prefer providers with transparent sourcing and regular audits.
Consent Considerations
Do you need consent to enrich?
- B2B context: Generally no explicit consent required under legitimate interest
- B2C context: More stringent; may require consent
- Sensitive data: Never enrich sensitive categories (health, financial, political)
Best practice: Consult legal counsel for specific use cases and jurisdictions.
Cost vs Value: ROI of Enrichment
Enrichment has real costs. Make sure you're getting positive ROI:
Typical Costs
Per-lead pricing: $0.10 - $1.00 per enriched lead (varies by provider and volume) Subscription pricing: $1,000 - $10,000/month for unlimited enrichment Credit-based pricing: Buy credit packs, consume per enrichment
Cost optimization strategies:
- Enrich only qualified leads (after initial screening)
- Deduplicate before enriching (avoid enriching duplicates)
- Use progressive profiling for low-intent sources
- Negotiate volume discounts with providers
Value Calculation
ROI formula:
Value of Enrichment = (Increased Conversion Rate × Lead Volume × Average Deal Size) - Enrichment Cost
Example:
- Lead volume: 1,000/month
- Conversion rate improvement: 5% (from 15% to 20%)
- Average deal size: $10,000
- Additional revenue: 50 additional deals/year × $10,000 = $500,000
- Enrichment cost: $0.50/lead × 12,000/year = $6,000
- Net value: $494,000
- ROI: 8,133%
Variables to measure:
- Conversion rate improvement (enriched vs. non-enriched cohorts)
- Sales rep time savings (reduced manual research)
- Routing accuracy improvement (right rep assignment)
Implementation Checklist
Here's how to deploy lead enrichment systematically:
Phase 1: Provider Selection
- Define required data fields (prioritized)
- Test 2-3 providers on sample lead data
- Compare match rates, accuracy, and cost
- Review privacy/compliance certifications
- Negotiate pricing and contract terms
Phase 2: Integration Development
- Integrate provider API with lead capture flow
- Implement field mapping and data normalization
- Build error handling and fallback logic
- Configure enrichment timing (real-time vs batch)
- Test end-to-end with sample leads
Phase 3: Routing & Scoring Updates
- Update lead scoring model with enriched fields
- Build routing rules leveraging enriched data
- Create ICP filters using firmographic data
- Configure territory routing based on company location
Phase 4: Monitoring & Optimization
- Track enrichment match rates and costs
- Monitor data quality (accuracy audits)
- Measure conversion rate impact
- Gather sales feedback on data usefulness
- Optimize enrichment timing and field selection
The Bottom Line
Lead enrichment turns incomplete form submissions into actionable sales intelligence. It's what makes sophisticated qualification, personalized engagement, and efficient routing actually work.
Organizations that enrich leads systematically see:
- 20-30% higher conversion rates through better qualification (Datamaticsbpm B2B Data Solutions)
- 15-25% faster response times through automated routing
- Up to 500 fewer hours per rep per year wasted on researching bad prospect data (DealSignal)
Skip enrichment and you're forcing sales teams to manually research every lead. That means delayed follow-up, missed hot leads, and wasted sales time.
The data gap between capture and action determines whether leads convert or disappear. Enrichment closes that gap.
Ready to implement systematic enrichment? Explore lead scoring systems to leverage enriched data and lead distribution strategy for sophisticated routing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What percentage of CRM data becomes inaccurate over time? Research from DealSignal shows that 70% of CRM data is outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate at any given point. The underlying driver is decay rate: B2B contact databases lose validity at roughly 2.1% per month (IndustrySelect), which means that without ongoing enrichment, more than a fifth of your database is unreliable within a year.
How much does poor data quality cost the average organization? Gartner estimates that poor data quality costs the average organization $12.9 million per year. Those losses compound through wasted sales time, misdirected marketing spend, and missed revenue from leads that were disqualified based on wrong firmographic data. A separate IBM study cited by IndustrySelect puts the total U.S. economy-wide cost at $3.1 trillion annually.
How fast do job titles and contact details change in a B2B database? Faster than most teams assume. IndustrySelect's analysis of B2B contact databases found that 65.8% of job titles change in a given year, 42.9% of phone numbers change, and 37.3% of email addresses become invalid. This means a contact record that is accurate today may be wrong in three to six months without a re-enrichment cycle.
What ROI can companies expect from lead enrichment? Companies addressing CRM data decay through enrichment see a 15% improvement in close rates and a 20% improvement in campaign response rates within six months, according to SMARTe research. The ROI math is straightforward: DealSignal data shows reps waste approximately 500 hours per year on bad prospect research - enrichment converts much of that time back into selling.
Do sales reps actually spend significant time researching leads manually? Yes - and it's a larger problem than most organizations track. DealSignal's research found that sales reps lose approximately 500 hours annually (equivalent to 62 full working days) to correcting bad prospect data and manually hunting for information that enrichment tools deliver instantly. At average sales rep salaries, that amounts to roughly $32,000 in wasted productivity per rep per year (IndustrySelect).
What match rate should I expect from a B2B data enrichment provider? Expect meaningful variation depending on the lead type. B2B work email addresses typically achieve 70-85% match rates against major provider databases. Established companies with 500 or more employees match at 90-95% on company domain. Startups and SMBs drop to 60-75%. Independent testing cited by DealSignal found that most B2B data vendors deliver roughly 50% accuracy on average - making provider evaluation on your actual lead sample essential before committing to a contract.
Is enriched data compliant with GDPR for B2B outreach? In a B2B context, enriching business contact data for business outreach generally falls under "legitimate interest" as a lawful basis under GDPR - meaning explicit consent is not always required. But compliance depends on three conditions: you can document a genuine legitimate interest, the processing is proportionate, and the individual's interests don't override yours. You should maintain a Data Processing Agreement (DPA) with any enrichment provider and ensure your privacy policy discloses enrichment practices. Consult legal counsel for jurisdiction-specific requirements, particularly for contacts in regulated industries or with consumer data mixed in.
Related Resources
Lead Capture & Generation
- Lead Sources Overview - Understand where leads originate
- Landing Page Lead Capture - Optimize your form strategy
- Multi-Channel Lead Capture - Capture leads across channels
- Inbound Lead Generation - Attract qualified prospects
Lead Qualification & Scoring
- Lead Qualification Frameworks - BANT, MEDDIC, and beyond
- Types of Leads - Understanding lead taxonomy
- Lead Lifecycle Stages - Map the buyer journey
Lead Distribution & Routing
- Round-Robin Assignment - Fair lead distribution
- Weighted Lead Distribution - Performance-based routing
- Lead Assignment SLA - Set routing standards
Lead Operations
- Lead Data Management - Build a clean database
- Lead Status Management - Track lead progression
- Lead Recycling Strategies - Re-engage cold leads

Tara Minh
Operation Enthusiast
On this page
- What is Lead Enrichment?
- Why Enrichment Matters: Four Operational Outcomes
- 1. Better Qualification
- 2. Improved Personalization
- 3. Faster Routing
- 4. Higher Conversion
- What Data Should You Enrich?
- Contact-Level Data (Individual)
- Company-Level Data (Firmographic)
- Technographic Data
- Intent Signals
- How to Enrich Lead Data
- 1. Manual Research (Low Scale, High Quality)
- 2. Progressive Profiling (Over Time)
- 3. Third-Party Data Providers (Scale + Automation)
- 4. Reverse IP Lookup (Company Identification)
- 5. Social Enrichment
- When to Enrich: Timing Strategies
- At Capture (Real-Time)
- After Capture (Batch)
- Before Routing (Enrichment Gate)
- Before Sales Touch (Just-in-Time)
- Data Quality: Accuracy, Freshness, Completeness
- Match Rates (What Percentage of Leads Can Be Enriched?)
- Data Accuracy (How Correct is Enriched Data?)
- Data Freshness (How Current is the Data?)
- Completeness (How Many Fields Are Populated?)
- Privacy & Compliance: GDPR, Consent, Data Sources
- GDPR Compliance
- Data Source Transparency
- Consent Considerations
- Cost vs Value: ROI of Enrichment
- Typical Costs
- Value Calculation
- Implementation Checklist
- The Bottom Line
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Resources
- Lead Capture & Generation
- Lead Qualification & Scoring
- Lead Distribution & Routing
- Lead Operations